The global precision diagnostics market size was valued at USD 76.19 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 270.31 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.5% from 2024 to 2033.
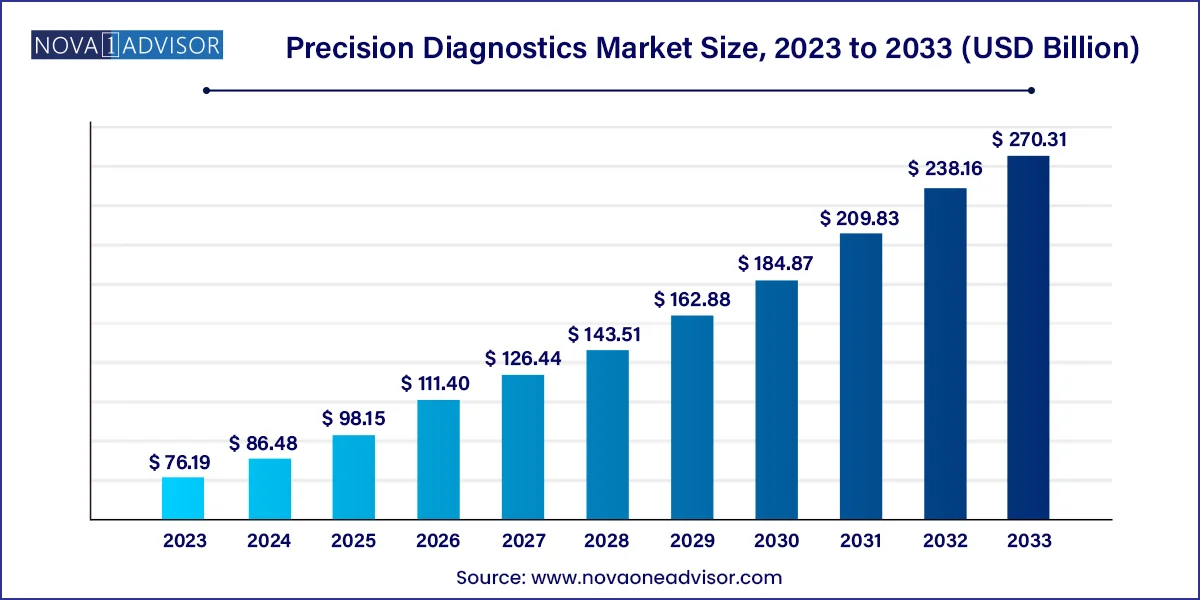
The U.S. precision diagnostics market size surpassed USD 26.23 billion in 2023 and is projected to attain around USD 97.19 billion by 2033, poised to grow at a CAGR of 12.73% from 2024 to 2033.
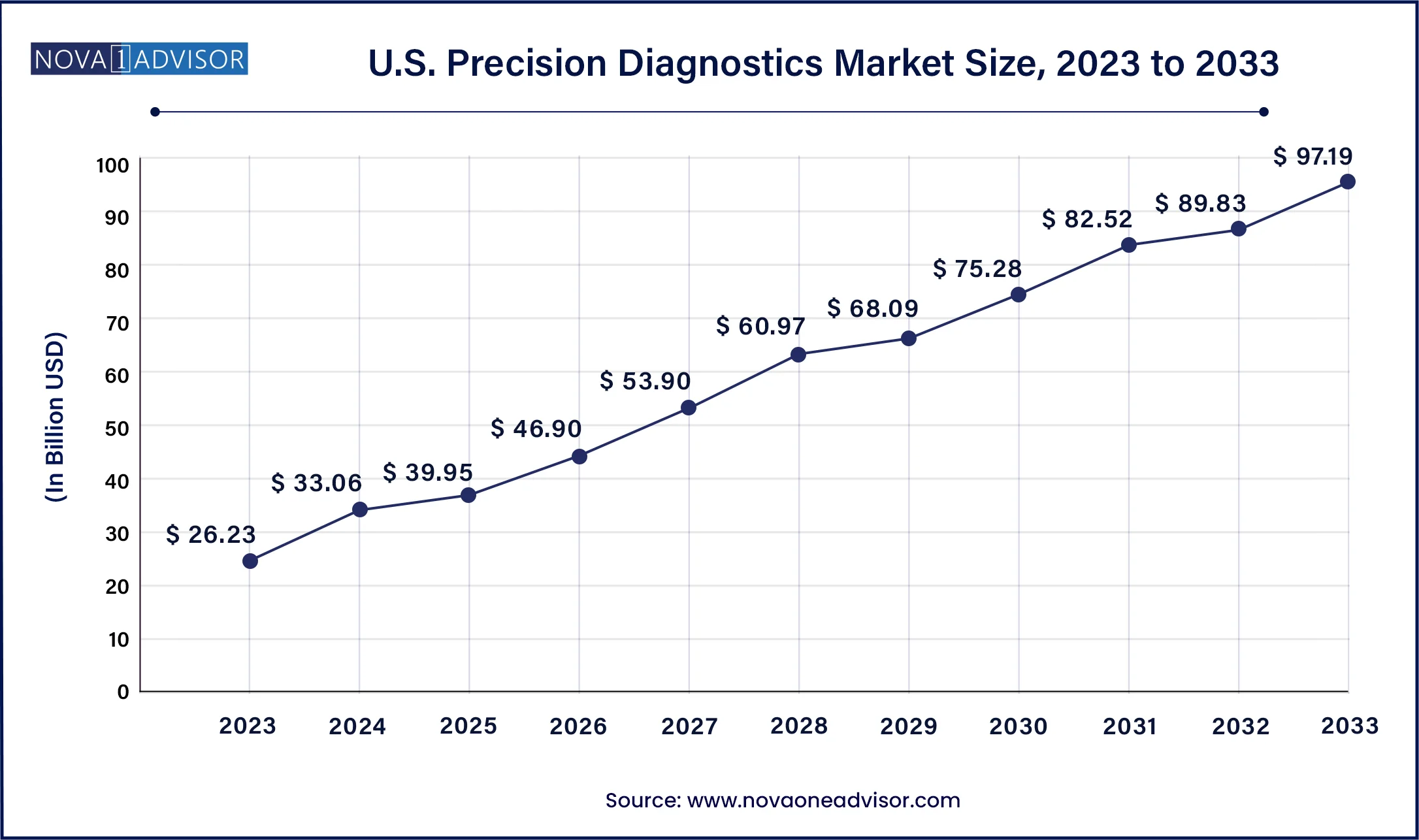
North America leads the global precision diagnostics market, driven by a robust innovation ecosystem, regulatory clarity, and widespread reimbursement coverage. The U.S., in particular, benefits from a confluence of factors including advanced genomics infrastructure, significant R&D investment, and supportive policies from the FDA and CMS. Private and public payers are increasingly covering precision tests, particularly in oncology and rare diseases. Leading institutions such as the Mayo Clinic, UCSF, and Dana-Farber are spearheading research, and biotech hubs in Boston, San Diego, and the Bay Area are hotbeds of diagnostic innovation.
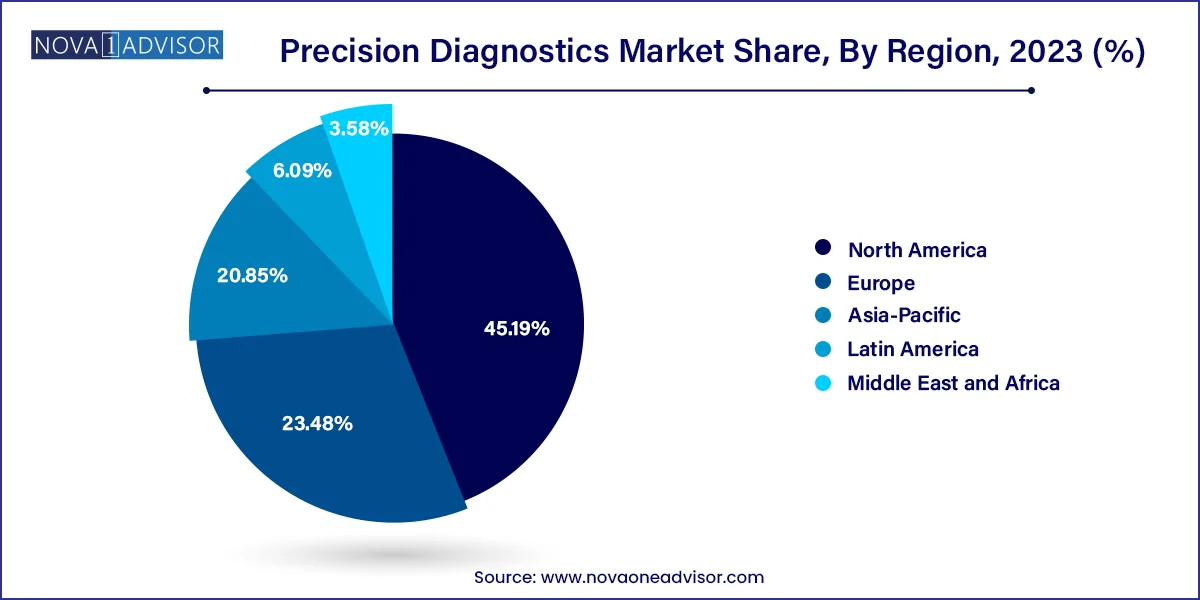
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by investments in personalized medicine, growing awareness, and the expansion of genomic initiatives. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are accelerating national genome sequencing programs, strengthening healthcare IT infrastructure, and fostering public-private partnerships. In China, precision medicine is a national strategic priority, with over $9 billion allocated for genomics research. Meanwhile, India’s growing diagnostic industry and government initiatives like IndiGen are helping integrate genetic testing into population health strategies. The region is also home to several startups and diagnostics platforms that are rapidly scaling in both domestic and export markets.
The precision diagnostics market is emerging as a transformative force in the global healthcare ecosystem. Precision diagnostics refers to the suite of advanced diagnostic tools and technologies that enable the detection and characterization of diseases at a molecular or genetic level, allowing for highly tailored therapeutic decisions. In contrast to traditional diagnostic methods, precision diagnostics aim to deliver individualized, real-time insights into disease pathology, progression, and likely treatment response—essentially serving as the cornerstone of precision medicine.
With the rapid evolution of genomics, proteomics, and data analytics, the field of diagnostics has undergone a paradigm shift. Innovations such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), liquid biopsies, and multi-omics platforms now empower clinicians to detect disease biomarkers early, track tumor mutations in real time, and assess hereditary disease risks with unprecedented accuracy. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the integration of molecular diagnostics into routine care and public health strategies, bolstering awareness and infrastructure that is now being leveraged for broader precision health applications.
Key market players including Illumina, Roche, Guardant Health, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitae, and Exact Sciences are aggressively expanding their portfolios and forming strategic alliances to maintain competitiveness. Government support, patient advocacy, and increased payer acceptance for biomarker-based therapies continue to drive the adoption of precision diagnostics in clinical workflows. As personalized healthcare models evolve and genomic technologies become more cost-effective, the precision diagnostics market is poised for sustained growth and innovation across oncology, immunology, neurology, and rare diseases.
Rise of liquid biopsies and non-invasive diagnostics: Liquid biopsy platforms are rapidly gaining acceptance due to their ability to detect cancer biomarkers from blood samples.
Growing adoption of multi-omics approaches: Combining genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics for comprehensive disease insights is driving integrated diagnostics.
Expansion of direct-to-consumer (DTC) testing: Genetic and wellness testing kits are becoming popular among health-conscious consumers, especially in the U.S.
AI and machine learning integration in diagnostic workflows: Predictive analytics and pattern recognition are enhancing diagnostic precision and reducing interpretation times.
Increased investment in companion diagnostics (CDx): Pharma-diagnostic partnerships are rising to co-develop targeted therapies and diagnostics.
Regulatory evolution supporting advanced diagnostics: Agencies like the FDA are providing expedited approval pathways for breakthrough diagnostic technologies.
Decentralization of testing: Home-based testing, point-of-care platforms, and mobile diagnostics are enabling broader access to precision diagnostics.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 86.48 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 270.31 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 13.5% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Type, application, end-use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Abbott Laboratories; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Siemens Healthineers AG; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; bioMérieux SA; Becton, Dickinson and Company; Danaher Corporation; QIAGEN N.V.; Hologic Inc.; Agilent Technologies Inc. |
A primary driver fueling the precision diagnostics market is the growing emphasis on precision medicine in oncology. Cancer is inherently heterogeneous, meaning that even patients with the same tumor type can have vastly different genetic and molecular profiles. Precision diagnostics play a pivotal role in profiling tumors, identifying actionable mutations, and guiding targeted treatment strategies. This shift has moved cancer care away from a "one-size-fits-all" model to one where therapies are customized based on individual tumor biology.
For example, Guardant Health launched Guardant360 CDx, an FDA-approved liquid biopsy companion diagnostic for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. This test identifies EGFR mutations from a blood draw, informing decisions on EGFR-targeted therapies. Similarly, Foundation Medicine's FoundationOne CDx is widely used across multiple cancer types to match patients with approved immunotherapies and investigational trials. These advances are revolutionizing the way clinicians detect and manage cancer, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs associated with ineffective treatments. As oncology pipelines increasingly rely on biomarkers for drug efficacy, precision diagnostics will continue to grow in clinical significance and commercial demand.
Despite its promise, the precision diagnostics market faces significant challenges surrounding patient data privacy and complex regulatory oversight. Precision diagnostics often involve sensitive genetic information, which, if improperly handled, can lead to serious ethical and legal consequences. Data breaches or misuse of genomic data could result in discrimination in insurance, employment, or social stigmatization.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape for diagnostic products particularly in multi-omic and AI-powered tests is still evolving. Developers must navigate varying standards for analytical validity, clinical utility, and data management across jurisdictions. The FDA's approach to laboratory-developed tests (LDTs) and the European Union’s In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) reflect increasing scrutiny, which may delay market access and add to compliance costs. Smaller diagnostic developers often struggle to meet regulatory demands while maintaining commercial viability. As the industry matures, stakeholders will need to establish robust data governance and harmonize regulatory frameworks to foster innovation while protecting public trust.
One of the most promising opportunities in the precision diagnostics market lies in the rise of population genomics and proactive disease risk screening. Rather than focusing solely on disease diagnosis, healthcare systems are shifting toward predictive and preventive models an area where precision diagnostics are indispensable. By analyzing genetic predispositions to conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders, population-wide genomic screening programs can significantly reduce disease burden through early intervention.
In the U.S., initiatives like the All of Us Research Program aim to collect health data from over 1 million Americans to advance individualized prevention and treatment strategies. Companies like Color Genomics and Invitae are offering affordable hereditary cancer screening panels, often bundled with genetic counseling, for population-scale deployment. As these programs become embedded in public health policy and insurance reimbursement expands, the market for predictive and preventive diagnostics will experience substantial growth. This shift not only improves outcomes but also opens up new revenue models through subscription-based risk monitoring and longitudinal health tracking.
Genetic tests dominated the precision diagnostics market, driven by their utility in identifying hereditary diseases, cancer mutations, pharmacogenomic markers, and prenatal anomalies. With declining sequencing costs and expanded consumer interest, genetic tests are increasingly incorporated into routine clinical decision-making. Platforms like Illumina’s TruSight and Myriad Genetics’ myRisk assess germline mutations for hereditary cancer risk, while pharmacogenomic panels are being used to tailor medications based on CYP450 enzyme activity. Hospitals and primary care providers are also beginning to adopt preemptive genetic testing for actionable conditions.
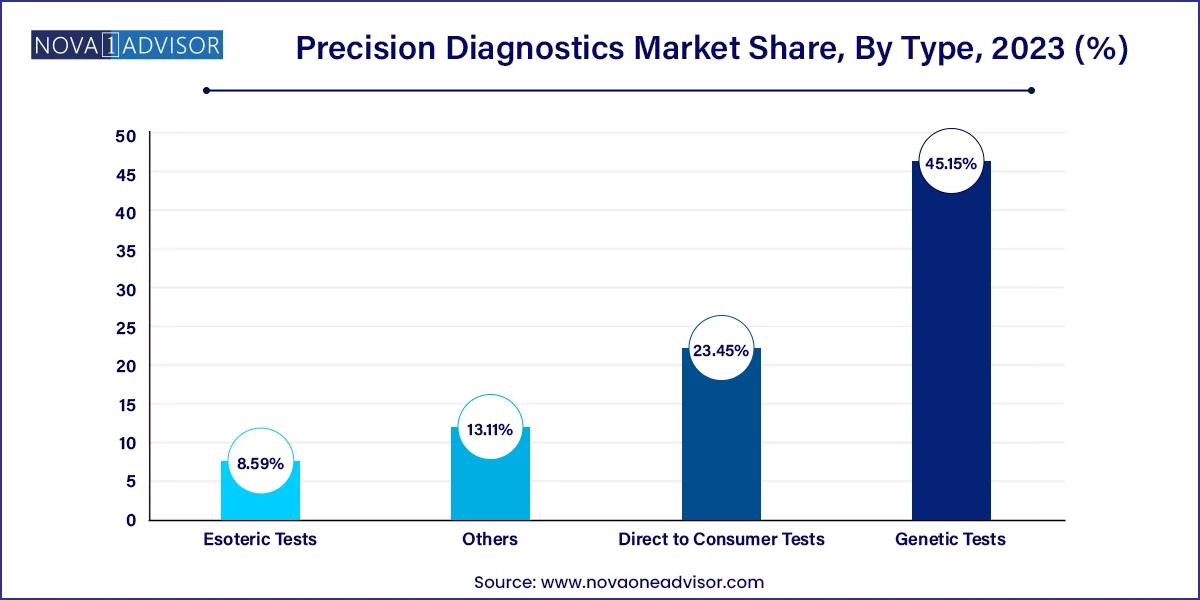
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) tests represent the fastest-growing type segment, reflecting the convergence of personalized healthcare, digital commerce, and consumer empowerment. Companies like 23andMe, AncestryDNA, and Everlywell offer kits for ancestry, health traits, and genetic risk predispositions. More recently, the market has seen a shift toward clinically validated DTC offerings that provide medical-grade insights and integrate physician consultation. This evolution is expected to continue as consumers seek greater autonomy over their health data and testing processes.
Oncology applications dominate the precision diagnostics market, given the growing reliance on biomarker-based decision-making in cancer care. Diagnostic assays such as PD-L1 testing, BRCA mutation panels, and tumor mutation burden (TMB) profiling are now standard tools in oncology clinics. FDA approvals increasingly depend on companion diagnostics, with nearly 50% of all oncology drug approvals linked to specific biomarkers. Companies like Exact Sciences and Foundation Medicine are at the forefront, offering multi-cancer early detection tests and comprehensive genomic profiling.
CNS disorders represent the fastest-growing application segment, as neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric conditions increasingly demand biomarker support for diagnosis and treatment. The rise of transcriptomics, epigenomics, and neuroimaging-based biomarker integration is enabling earlier detection of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s, and schizophrenia. Startups and academic consortia are actively pursuing blood-based biomarker diagnostics, and AI-powered interpretation tools are being developed to assess cognitive and neurodevelopmental abnormalities. As research progresses, precision diagnostics will be key to managing neurological diseases that have historically lacked objective testing tools.
Hospitals and academic medical centers account for the largest end-use segment, due to their access to integrated electronic health records (EHRs), diagnostic infrastructure, and multidisciplinary teams. Most high-complexity precision tests such as whole-exome sequencing or next-generation panels are initiated within hospital settings where sample collection, interpretation, and follow-up care are coordinated. Moreover, large hospitals often act as clinical trial hubs, adopting the latest diagnostic technologies in tandem with drug development.
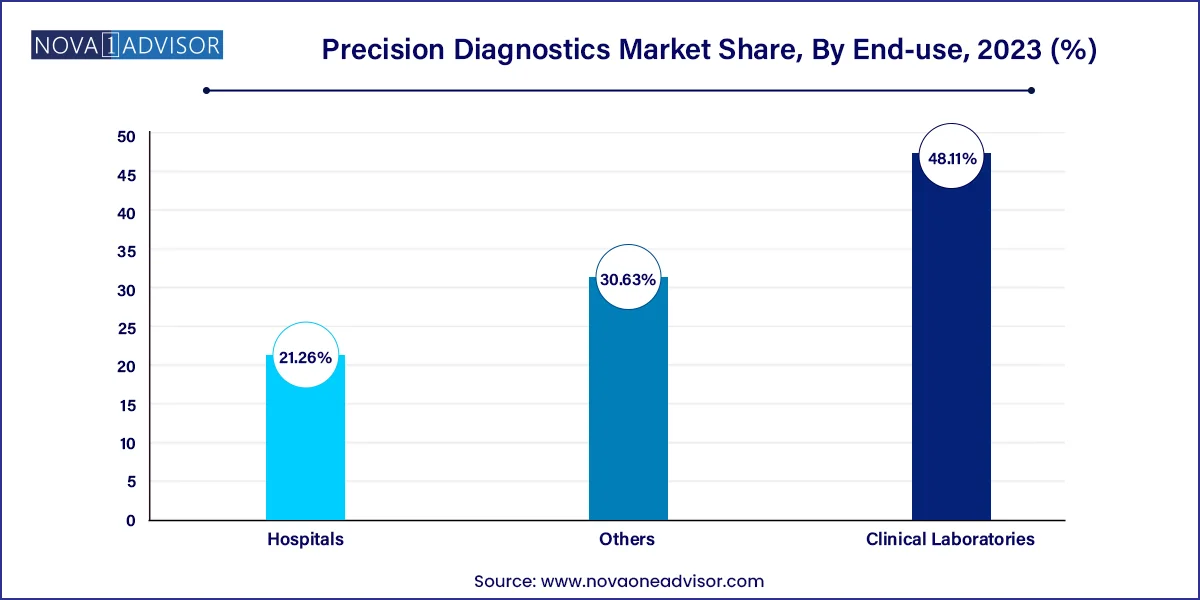
Clinical laboratories are the fastest-growing end-use segment, as more precision diagnostic tests shift from research to commercial service labs. Companies like Labcorp, Quest Diagnostics, and Guardant Health are expanding their molecular and genomic testing services, often offering test kits that can be ordered remotely and processed centrally. These labs serve both physicians and consumers, offering scalable, CLIA-certified testing platforms for oncology, infectious disease, and rare disorders.
The market players operating in the global market are adopting product approval to increase the reach of their products in the market and improve the availability of their products in diverse geographical areas, along with expansion as a strategy to enhance production/research activities. In addition, several market players are acquiring smaller players to strengthen their market position. This strategy enables companies to increase their capabilities, expand their product portfolios, and improve their competencies.
The following are the leading companies in the precision diagnostics market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Precision Diagnostics market.
By Type
By Application
By End-use
By Region